

Question marks are the most management-intensive products and require large investments and resources to increase their market share. Products in the question mark quadrant are in a market that is growing rapidly, but where the product(s) have a low market share. The market growth rate varies from industry to industry, but usually indicates a 10% demarcation point: growth rates above 10% are considered high, while those below 10% are considered low. A firm benefits from the use of economies of scale and gains a cost advantage over competitors. The matrix is based on the assumption that an increase in relative market share results in an increase in cash flow.
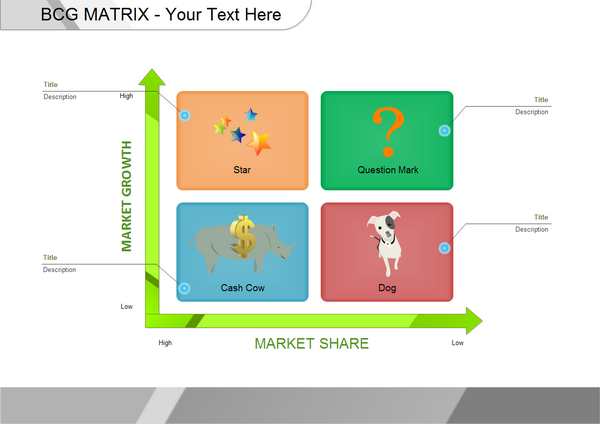
Milking cows: Products with low market growth but high market share.Dogs: Products with low market growth and low market share.Stars: Products with high market growth and high market share.Question marks: Products with high market growth but low market share.The vertical axis of the BCG matrix represents the growth rate of a product and its growth potential in a given market.įrom this the four quadrants are deduced: Using relative market share, it helps measure a company's competitiveness. The horizontal axis of the BCG matrix represents a product's market share and strength in a given market. Copyright Corporate Finance Institute Understanding the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix.

Each quadrant is classified as low or high performing, based on relative market share and market growth rate. It ranks a company's brands, products, and/or services in a two-axis matrix that forms 4 quadrants. The BCG matrix is one of the most widely used methods of analyzing the composition of corporate assets. The Boston Consulting Group matrix (BCG matrix), also called the product portfolio matrix, is a business planning tool used to assess the strategic position of a company's brand or product portfolio.
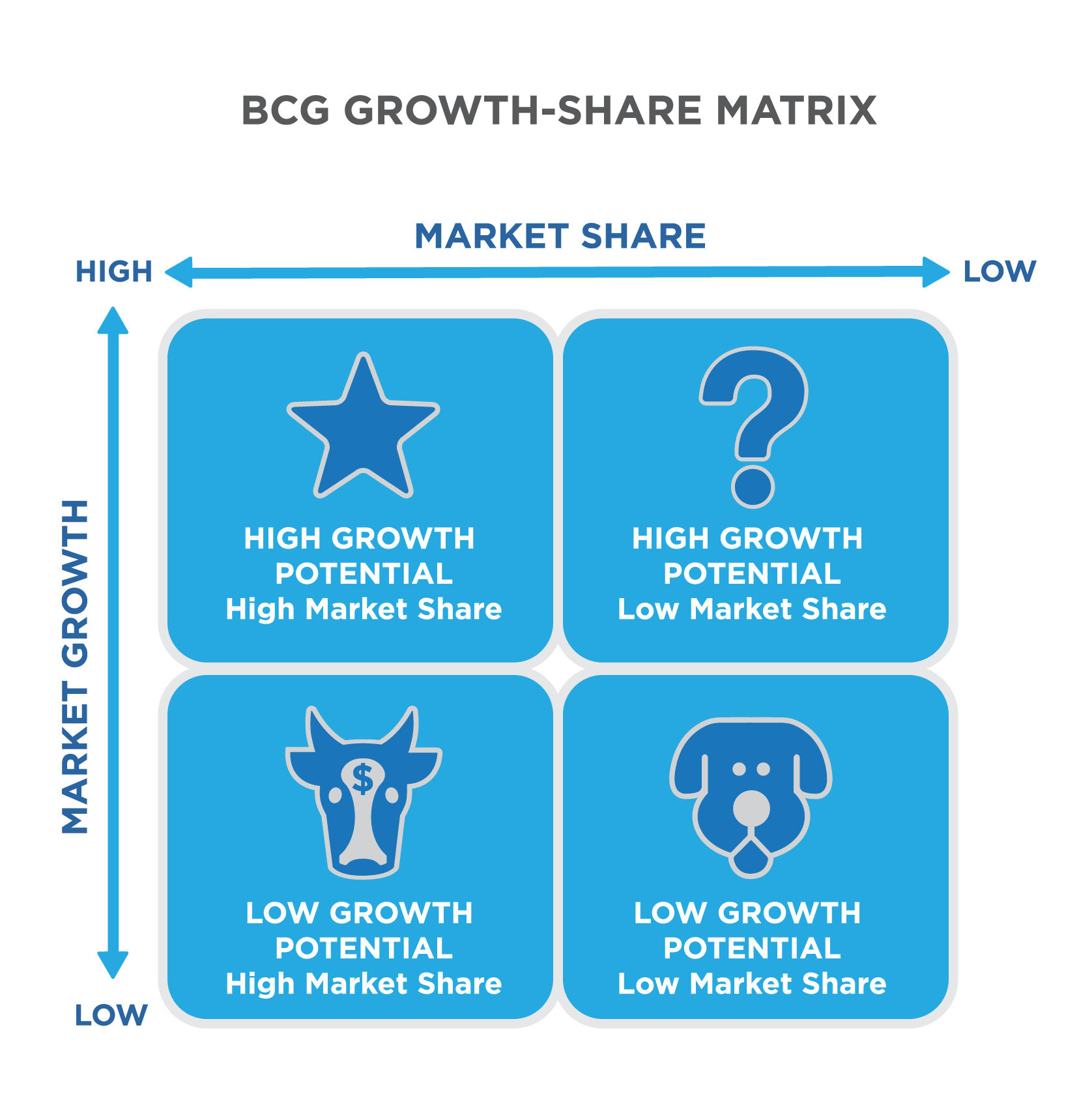
How to properly employ the BCG Matrix in strategies?.Understanding the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
